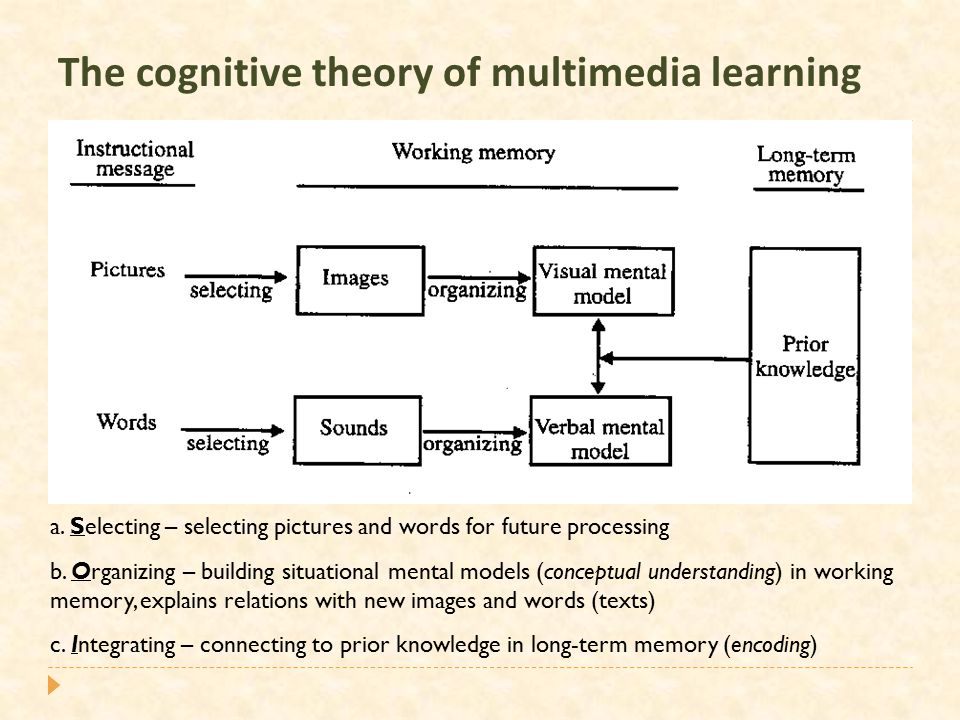
The Cognitive Theory Of Multimedya Learning (CTML)
"People learn more deeply from words and pictures than from words alone" (Mayer, p. 47). When a teacher uses visuals such as graphics, pictures or charts as well as verbal texts and informations, multimedia learning occurs and learning becomes easier and meaningful for a learner. The Cognitive Theory Of Multimedya Learning has three main assumptions to learn with multimedia:
- There are two separate channels (auditory and visual) for processing information. Images seen through the eyes and spoken words.
- Each channel has a limited (finite) capacity. "Mayer indicates that individuals at the higher end of that range may have stronger metacognitive strategies, which allow them to manage their limited cognitive resources more efficiently."¹
- Learning is an active process of filtering, selecting, organizing, and integrating information based upon prior knowledge.